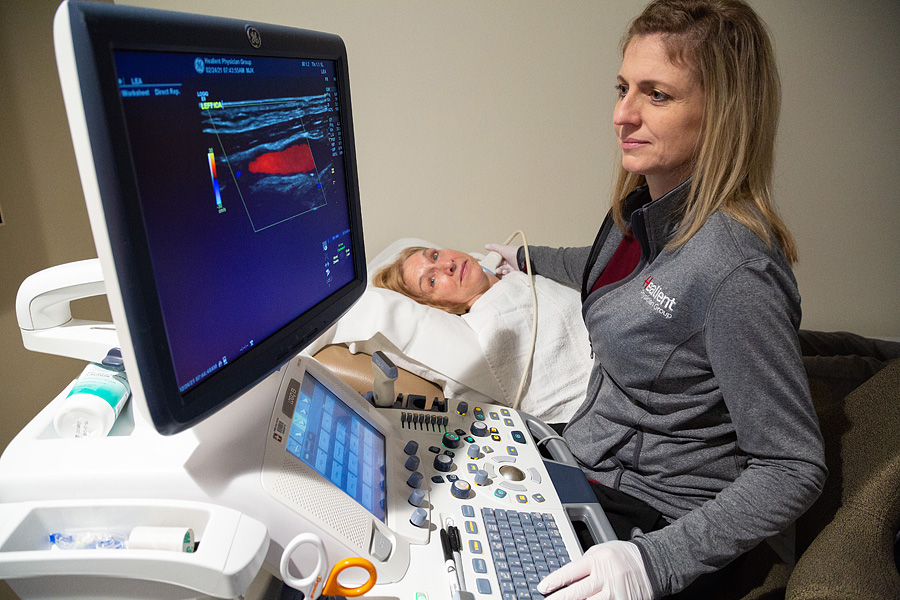
There are many tests a vascular physician might order to help identify common vascular conditions. These non-invasive tests use ultrasound to measure the amount of blood flow in your arteries and veins. These tests help our physicians diagnose a patient’s condition and create a treatment plan.
Healient Physician Group has its own vascular testing lab in the heart of its clinic. We partner with St. Joseph Medical Center to provide this state of the art imaging center.
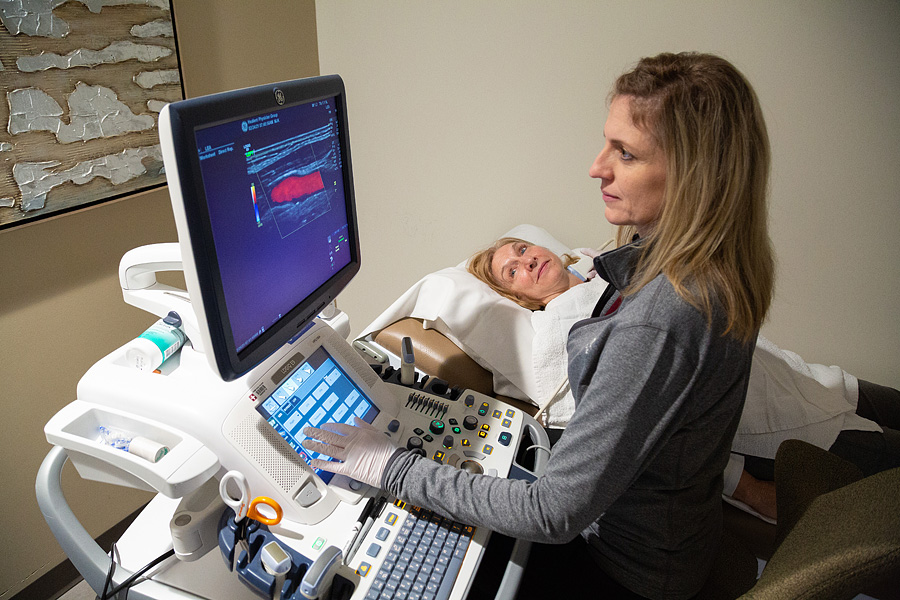
Our vascular techs have over 20 years of experience, which means their exams are very accurate and precise.
If your doctor suspects vascular disease, they may order non-invasive vascular testing. These are simple and painless tests using ultrasound to determine the presence, location, and severity of vascular disease.
A duplex ultrasound combines traditional ultrasound images combined with Doppler ultrasound-derived flow information. Doppler ultrasound records sound waves reflecting off moving objects, such as blood, which can be used to measure its speed and flow direction, which can demonstrate the severity of narrowing in a variety of vessels.
Testing and Diagnosis of Common Vascular Conditions
Testing and Diagnosis of AAA is usually accomplished with abdominal ultrasound, CT, or CT angiography.
Testing and Diagnosis for TAA involving the ascending aorta may be done with cardiac ECHO. However CT angiography is typically the best test to fully evaluate the entire thoracic aorta for a TAA.
Testing and Diagnosis of IAA is usually accomplished with abdominal ultrasound, CT, or CT angiography.
Testing and Diagnosis for PAD is easy with a physical exam by a vascular physician. Ankle-branchial index or ABI is a simple test which compares the blood pressure in your ankle with the bloo pressure in your arm. Ultrasound or sonography can be used to directly image the arteries to identify an arterial blockage. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) angiography are noninvasive methods of creating a “road map” of the arteries to identify the narrow areas. Catheter-based angiography involves placing a tiny tube inside the artery to give highly detailed pictures of your arterial anatomy.
Testing and Diagnosis of PAA are usually accomplished with ultrasound, CT, or CT angiography.
Testing and Diagnosis for VAA is most often done with ultrasound, CT, or CT angiography. Catheter-based angiography may be performed if surgical treatment is anticipated.
Testing and Diagnosis usually begins with an ultrasound exam to asses the blood flow and velocity in the carotid arteries in the neck. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) angiography are noninvasive methods of creating a “road map” of the arteries of the neck and head to identify the narrow areas. Catheter-based angiography may also be used for a definitive demonstration of the anatomy.
Testing and Diagnosis for subclavian artery disease is starts with a physical exam by a vascular physician. Blood pressure measurements in both arms will be compared. Ultrasound can directly image the area of blockage in the subclavian artery.
Testing and Diagnosis for renal artery disease begins with a physical exam by a cardiovascular physician. Duplex ultrasound may help identify blockages in the kidney arteries. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) angiography are noninvasive methods of creating a “road map” of the arteries to identify the narrow areas. Catheter-based angiography involves placing a tiny tube inside the artery to give highly detailed pictures of your arterial anatomy.
Testing and Diagnosis for mesenteric artery ischemia may include duplex ultrasound to determine the presence of arterial blockage. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) angiography are noninvasive methods of creating a “road map” of the arteries to identify the narrow areas. Catheter-based angiography involves placing a tiny tube inside the artery to give highly detailed pictures of your arterial anatomy.
Testing and Diagnosis for chronic venous insufficiency depends primarily upon venous ultrasound studies. To evaluate for iliac vein narrowing which is the primary venous outflow pathway of the legs, venography and intra-vascular ultrasound is often used.
Testing and Diagnosis for vertebral compression fractures initially is with a plain X-ray or computed tomography (CT). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is helping in determining the age of the fracture, and in discovering subtle fractures which may be missed on X-ray.
Our Testing Process
Here’s how our testing process works.
Step 1. Get the testing order from your doctor.
Step 2. Schedule appointment with Healient.
Step 3. Follow instructions to prepare for the test.
Step 4. Perform the test at Healient's vascular testing lab.
Step 5. Discuss results with physician.
Meet your specialist.
Our Diagnosis Process
Here’s how our diagnosis process works.
Step 1. After test, discuss results with your physician.
Step 2. Implement a plan of treatment.
Step 3. Follow up with physician to evaluate effectiveness of plan.
